What are the differences between various coconut oils on the market?
Confused by coconut oil choices? Virgin? Refined? They are not the same. Learn how they differ.
Coconut oils vary mainly by processing method. Virgin oil uses minimal heat, keeping more nutrients. Refined oil uses heat and chemicals for neutral flavor and higher smoke point.



Understanding how each oil is made helps you choose the right one. Let’s look closer at how they get made.
How is Virgin Coconut Oil different from Refined Coconut Oil?
Want pure coconut goodness? Virgin coconut oil might be for you. But how is it made differently?
Virgin coconut oil usually comes from fresh coconut meat without chemicals or high heat. Refined oil comes from dried coconut and uses processing steps like bleaching and deodorizing.
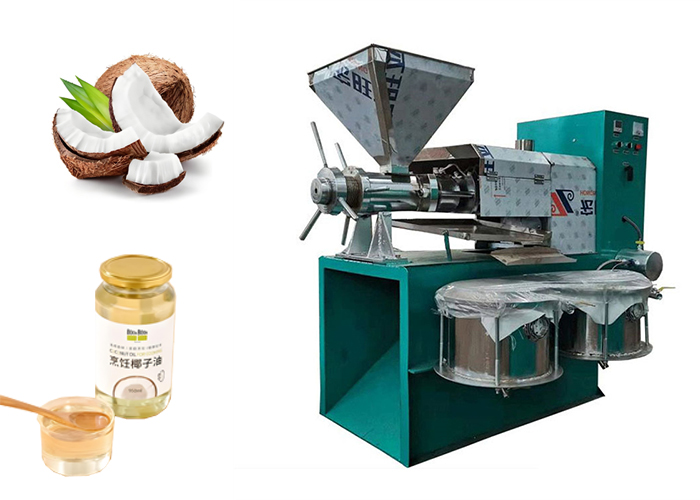

Virgin coconut oil uses mechanical methods. This is like wet milling or cold pressing. These methods use low heat. They preserve the natural aroma and flavor of coconut. The oil keeps more natural compounds. It has a strong coconut smell and taste. It also has a lower smoke point. This means it is best for low-heat cooking or not cooking at all.
Refined coconut oil is different. It starts with dried coconut meat. This is called copra. Copra needs oil extraction. Our screw presses work well for this. This makes crude coconut oil. This crude oil is then refined. Refining has steps. These steps use heat and sometimes chemicals. The steps are usually degumming or neutralization. Then it is bleached. Then it is deodorized. Our refining equipment does these steps. This process removes impurities. It takes away color. It removes the strong coconut smell and taste. This gives a neutral oil. It has no flavor. It has a higher smoke point. It is good for frying and high-heat cooking. Refined oil loses some nutrients during processing. It is solid at room temperature.
Making Virgin Coconut Oil
- Fresh coconut meat is used.
- Mechanical extraction methods are used. These are like wet milling or cold pressing.
- No chemicals are used. Low heat is used.
- The oil has a strong coconut smell. It tastes like coconut.
- It has a lower smoke point. This is about 350°F or 175°C.
- It keeps more natural compounds. It has antioxidants.
Making Refined Coconut Oil
- Dried coconut meat is used. This is called copra.
- Pressing extracts the oil. This can use high heat.
- Refining steps happen. These are bleaching and deodorizing.
- The oil has no smell. It has no taste. It is neutral.
- It has a higher smoke point. This is about 400°F or 200°C.
- It has fewer nutrients. Some are lost in processing.
What process makes RBD Coconut Oil?
You see RBD coconut oil everywhere. What does RBD mean? How do they make it?
RBD stands for Refined, Bleached, Deodorized. This process uses heat, bleaching clay, and steam to remove color, odor, and impurities from crude coconut oil.
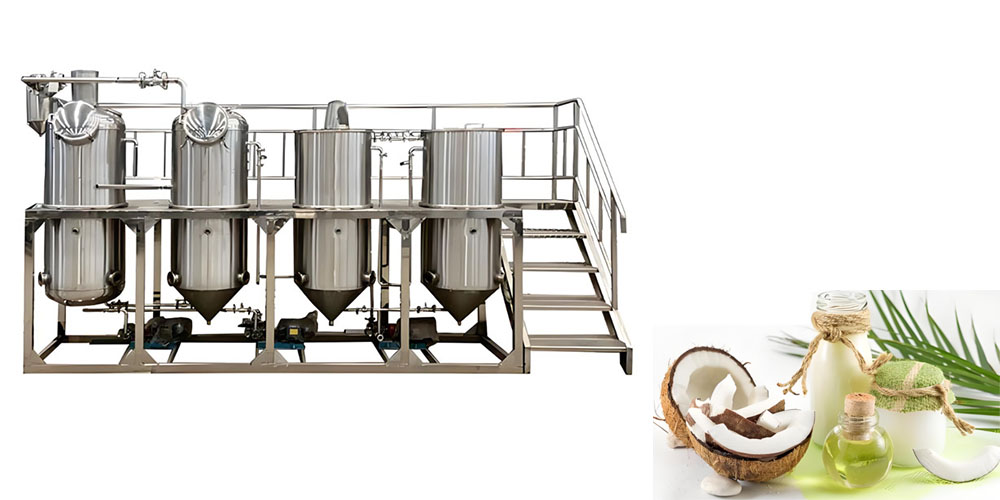

RBD production starts with crude coconut oil. This oil comes from pressing copra. Crude oil has impurities. It has strong color. It has a strong smell. Refining removes these unwanted things. The first step is often neutralization. This removes free fatty acids. It can use alkali. Our refining tanks are used here. Then bleaching happens. Bleaching uses clay. Clay absorbs pigments. This takes out the color. Our bleaching equipment helps. Next is deodorizing. This uses steam. Steam goes through the hot oil. It removes things that cause bad smell and taste. We have intermittent and continuous deodorizers. These are part of our refining equipment line. Finally, the oil is filtered. This removes any solid bits. This multi-step process gives RBD oil. It is a clean oil. It is solid at room temperature. But it is clear and has no smell or taste. It is very stable. This makes it good for food factories. It is used in baking, confectionery, and margarines. It is also used in soaps and cosmetics. It provides a consistent base.
| Step | Purpose | Equipment Involved (Relevant to Fude) |
|---|---|---|
| Neutralization | Remove free fatty acids | Refining tanks, Centrifuges |
| Bleaching | Remove color pigments | Bleaching tanks, Filters |
| Deodorizing | Remove odor and taste compounds | Deodorizers (batch or continuous) |
| Filtering | Remove solids, clay, and other particles | Filters (plate, leaf, bag) |
What is Fractionated Coconut Oil used for?
Ever seen liquid coconut oil that stays liquid? That is fractionated. What makes it special?
Fractionated coconut oil is made by heating coconut oil and cooling it to separate fats. It stays liquid at room temperature because long-chain fats are removed.

Coconut oil has different fatty acids in it. Some fats become solid at different temperatures. Fractionation is a way to separate these fats. The process starts by heating coconut oil. This melts all the fats. Then they cool it slowly. This controlled cooling makes the fats with higher melting points turn solid. These solid fats are called stearine. The fats with lower melting points stay liquid. This liquid part is collected. This liquid part is fractionated coconut oil. It is mostly medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs). It is often called MCT oil. It is always liquid at room temperature. It has no color. It has no smell. It does not feel heavy or greasy. It is very stable. It does not spoil easily. This is a specialized process in oil refining. It is not cooking oil. It is used in many products. It is common in cosmetics. People use it in lotions, soaps, and hair products. It is a good carrier oil. People mix it with essential oils. It is also used in some health supplements because it is high in MCTs.
How Fractionation Works
- Coconut oil contains a mix of different fats.
- The oil is heated. All fats become liquid.
- The oil is cooled carefully. Some fats become solid first. These are the higher melting point fats.
- Other fats stay liquid. These are the lower melting point fats.
- The solid and liquid parts are separated. This can use filters or centrifuges.
- The liquid part is fractionated coconut oil.
Properties and Uses
- It is always liquid at room temperature.
- It has no color. It has no smell.
- It feels light and non-greasy.
- It is very stable. It has a long shelf life.
- It is mainly medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs).
- Uses: It is used in cosmetics. It is used in skincare products. It is used in hair care. It is a good massage oil. It is used as a carrier oil for essential oils. It is also used in some health supplements.
Different coconut oils come from different processing. This affects properties and uses. Zhengzhou Fude Machinery will provide you with equipment that suits your needs.
Related recommendations
-
How does the tea seed peeling machine production line work
403The large-scale tea seed peeling machine production line goes through steps such as feeding and conveying, peeling and separation, finished product collection and storage, and automation control
View details -
What is the use of dryer in agriculture
578Drying machines have broad application prospects and important value in agriculture.
View details -
Fully automatic oil press
523The fully automatic oil press is an efficient, fast, and automated device mainly used to extract oil from various plant seeds
View details -
What are the advantages and disadvantages of hydraulic oil press
571As a commonly used oil extraction equipment, hydraulic oil press has its unique advantages and disadvantages. Let me introduce it to you ,
View details
 Oil Press Equipment and Oil Refining Machinery for Sale – Start Your Oil Press Business
Oil Press Equipment and Oil Refining Machinery for Sale – Start Your Oil Press Business



